
What are the typical electro-acoustic variable reverberation systems
Recognize different forms of electro - acoustic variable reverberation systems
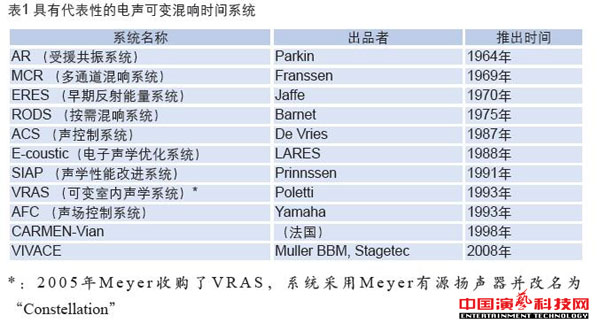
The use of electro-acoustic method to achieve the indoor acoustic variable practical system from the 20th century, 50 years. Since the advent of electro-acoustic reverberation system, with the development and progress of science and technology (especially the rapid development of electronic technology), from the beginning of the experimental device development to improve the system equipment, in many international developed countries, especially the theater Is a multi-functional theater has been a wider range of applications. Recognize the different forms of electro-acoustic variable reverberation system Table 1 lists a number of representative international electro-acoustic variable reverberation systems at different times in the world, their "mechanism" (including patented algorithms) and systems Are all different, and all of these systems can be represented by a normalized system block diagram.
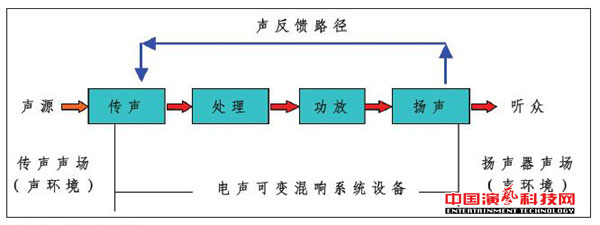
Normalized system block diagram
Brief introduction of typical electro - acoustic variable reverberation system
2.1 Resident Resonance (AR) systems
The Assisted Resonance system was developed by Parkin and Morgan in 1964 to improve the quality of the British Royal Festival Hall in London (mainly to increase the reverberation time in the hall) and developed a multi-channel reverberation system. The AR system is essentially a "narrowband" system, and each channel includes a condenser microphone, a frequency shifter, a 20 W power amplifier and a loudspeaker tuned to a narrow band with an acoustic resonator (Helmholtz resonator) 172 channels are used in the frequency range 58 Hz to 700 Hz.
AR system from the beginning of an experimental device after several years of continuous improvement and improvement, and ultimately became a permanent system equipment, it has become the longest multi-channel audio system, a successful case. Later in the United States some of the new concert halls (such as York, Concord and Scottsdale, etc.) also used the AR system, but the number of channels has been reduced.
2.2 multi-channel reverb (MCR) system
Holland Philips Franssen in the 1960s presented a series of "microphone-speaker independent broadband channels" that can significantly increase the indoor reverberation time. The multi-channel Reverberation system is the commercialization of the Franssen theory. MCR system has a practical application of more than 20 years of history, when many countries in Europe, new or modified multi-functional conference hall, multi-purpose theater and concert hall and other places have been widely used.
MCR system is the diffusion field as the object, so the microphone is arranged in the audience hall is not directly pick up the signal on the stage. The distance between each speaker and each microphone is outside the hall reverberation radius (especially the same channel microphone), so that the correlation between the channels can be minimized, the total amplification is the amount of each channel amplification Sum (energy sum). The system must strictly control the loop gain of each channel to ensure the stability of the system and the natural sense of the sound.

Application of the MCR system Lyon concert hall
2.3 Sound Control System (ACS)
Acoustic Control System (AcousticControl System) is the 20th century, 80 years by the Dutch company and the Dutch company Delft University jointly developed the electro-acoustic sound field control system. According to incomplete statistics, as of 2005, ACS has been in the rest of the world more than 50 theaters, multi-purpose theater, university auditorium, parliament hall and church and other places.

The California Grand Canyon Academy Theater, which uses the ACS system
ACS is the direct sound field as the object, so the microphone is arranged at the top of the stage directly pick up the signal on the stage, the use of the original signal and the system impulse response to add reverberation. Each directional microphone "responsible" pick up the stage or music part of the signal, usually a microphone covering 5 square meters to 10 square meters of the stage area. The signal picked up by each microphone is processed by the matrix device assigned to each channel.
2.4 Variable Indoor Acoustic System (VRAS)
The Variable RoomAcoustics Systems were developed by New Zealand M.A.Polt ti i in 1993 and developed by LCS (LEVEL CONTROL SYSTEMS). 2005 by the United States Meyer acquisition, VRAS renamed "Constellation".

Application of VRAS Prague Parliament Center Auditorium
VRAS is the most basic "coupling room" - the concept of electro-acoustic coupling, the core is a specially designed with a single nature of the "digital electronic reverb" instead of "true coupling space." Digital audio signal processor mainly includes: input cross-coupling matrix, multi-channel reverberator, feedback cross-coupling matrix, output cross-coupling matrix. This new non-direct-coupled system can naturally control both local and integral indoor acoustics compared to previous systems, and the reverberation gain of the system is independent of the loudness gain and can better suppress the possible sound staining to achieve high Quality sound reproduction.
2.5 Electronic Acoustic Optimization (E-coustic) system
In 1988, David Griesinger and Steve Barbar proposed "improving the indoor acoustics through time-varying artificial reverb", and the electronic acoustics optimization system was based on this theory, and the components and systems for acoustics optimization have been successfully designed and integrated. 1995 LARES company was established, the system in the software and hardware aspects of continuous improvement and improvement, the formation of todays new third-generation acoustic processing technology.
E-coustic system uses a new digital processing platform that is "independent time-varying reverb"), combined with the field of neuroscience and acoustics research results (sound quality and human perception of the relationship between) derived a new acoustic algorithm can be accurate Simulate all key acoustic parameters of the "room". The time-varying reverberator can broaden the resonant peak in the room transfer function, thereby increasing the stability of the system by at least 6 dB directly.
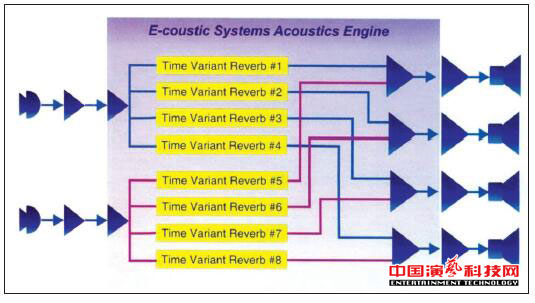
Independent time - varying channel diagram
The most important hardware part of the E-coustic system is the new Mainframe III (Matrix) and Matrix (Matrix) processors, which provide a system with extremely flexible acoustics processing capabilities. Mainframe III has four independent acoustic processing engines that run a new audio algorithm (derived from the latest research on physical acoustics and human neurology). Each acoustical processor independently controls the sound energy of direct sound, reflected sound and reverberation, and can adjust all key audio parameters (eg, mean free path, early decay time, etc.).

Application of the E-coustic system of the Toronto Elgin Theater
2.6 VIVACE system
VIVACE from Italian, meaning "lively". The VIVACE system was developed and improved in 2008 by two German companies, developed by Muller BBM Acoustics; the hardware was manufactured by Stagetec and eventually integrated into a complete VIVACE system.

Application of VIVACE system Mozart rock theater stage
VIVACE system uses the convolution algorithm, the system software also contains many of the worlds famous hall collected by the indoor acoustic characteristics of the parameters, with patented technology "acoustic fingerprint" project hall will be convoluted as the target hall of the acoustic characteristics of the parameters of the algorithm The stage signal is "folded" with the previously acquired impulse response. The system has four independent processing engines that can optimize and control the four different acoustic "regions" of the hall, respectively. Including the reverberation time, reverberation level, frequency characteristics, reflection density, transient response adjustment; and early reflection and reverberation sound independent control. The routing matrix in the system can set the level and time delay independently for each intersection, and supports 192 × 192 input / output at maximum. Relative to the traditional system, VIVACE system using a small number of microphones, usually only need 4 to 12. In addition, VIVACE system can be equipped with three-dimensional sound effects software, support live real-time multi-channel sound effects.








